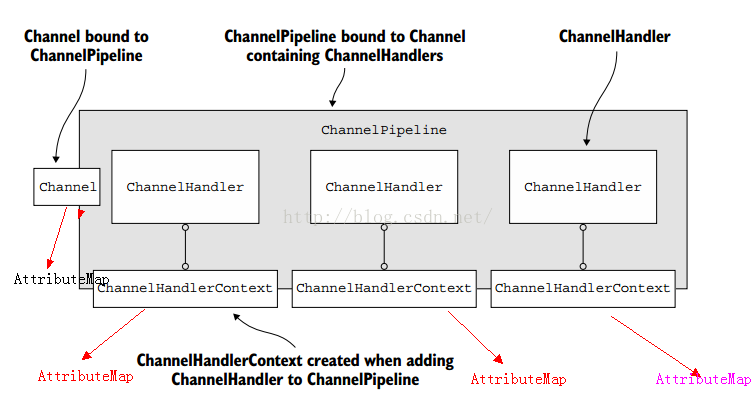
AttributeMap这是是绑定在Channel或者ChannelHandlerContext上的一个附件,相当于依附在这两个对象上的寄生虫一样,相当于附件一样,如图所示:

这个图还算比较形象地描述了AttributeMap的作用,我们知道每一个ChannelHandlerContext都是ChannelHandler和ChannelPipeline之间连接的桥梁,每一个ChannelHandlerContext都有属于自己的上下文,也就说每一个ChannelHandlerContext上如果有AttributeMap都是绑定上下文的,也就说如果A的ChannelHandlerContext中的AttributeMap,B的ChannelHandlerContext是无法读取到的
但是Channel上的AttributeMap就是大家共享的,每一个ChannelHandler都能获取到
我们再看看AttributeMap的结构:

可以看出这个是线程安全的,所以我们可以放心使用,再看看AttributeMap的结构,其实和Map的格式很像,key是AttributeKey,value是Attribute,我们可以根据AttributeKey找到对应的Attribute,并且我们可以指定Attribute的类型T:
我们可以这样使用:
1)首先定义一个AttributeKey:
public static final AttributeKey<NettyChannel> NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY = AttributeKey.valueOf("netty.channel");
我们AttributeMap中存储的是NettyChannel,这是我们自定义的一个类:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import java.util.Date;
public class NettyChannel {
private String name;
private Date createDate;
public NettyChannel(String name,Date createDate) {
this.name = name;
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
}
那么我们可以这么使用ChannelHandler中这么使用:
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
NettyChannel nChannel = attr.get();
if (nChannel == null) {
NettyChannel newNChannel = new NettyChannel("HelloWorld0Client", new Date());
nChannel = attr.setIfAbsent(newNChannel);
} else {
System.out.println("attributeMap 中是有值的");
System.out.println(nChannel.getName() + "=======" + nChannel.getCreateDate());
}
System.out.println("HelloWorldC0ientHandler Active");
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
channelActive方法中的ChannelHandlerContext方法可以使用attr方法传入AttributeKey获取一个Attribute,如果我们之前没有赋值,那么此时的Attribute值应该是null,我们就创建一个NettyChannel,并使用setIfAbsent这个方法,这个方法是线程安全的,大体的使用方法就是如此
现在我们举两个简单的例子
1)测试ChannelHandler上的AttributeMap是不是上下文绑定的------------首先我们在客户端写两个自定义的ChannelHandler方法,这两个方法的的ChannelActive都会在ChannelHandlerContext上的AttributeMap上写一些属性,然后在对应的ChannelRead方法上读取对应的值,看其是否能读取到:
我们先贴服务端的代码。很简单:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class HelloWorldServer {
private int port;
public HelloWorldServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap sbs = new ServerBootstrap().group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HelloWorldServerHandler());
};
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture future = sbs.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Server start listen at " + port );
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} else {
port = 8080;
}
new HelloWorldServer(port).start();
}
}
Channel:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class HelloWorldServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server channelRead..");
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"->Server :"+ msg.toString());
ctx.write("server write"+msg);
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端的bootstrap代码:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
public class HelloWorldClient {
static final String HOST = System.getProperty("host", "127.0.0.1");
static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8080"));
static final int SIZE = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("size", "256"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initChannel();
}
public static void initChannel() throws InterruptedException{
// Configure the client.
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new HelloWorldClientHandler());
p.addLast(new HelloWorld2ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush("hello Netty,Test attributeMap");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
一个常量类:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import io.netty.util.AttributeKey;
public class AttributeMapConstant {
public static final AttributeKey<NettyChannel> NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY = AttributeKey.valueOf("netty.channel");
}
两个客户端的handler:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import static com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap.AttributeMapConstant.NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.Attribute;
import java.util.Date;
public class HelloWorldClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
NettyChannel nChannel = attr.get();
if (nChannel == null) {
NettyChannel newNChannel = new NettyChannel("HelloWorld0Client", new Date());
nChannel = attr.setIfAbsent(newNChannel);
} else {
System.out.println("channelActive attributeMap 中是有值的");
System.out.println(nChannel.getName() + "=======" + nChannel.getCreateDate());
}
System.out.println("HelloWorldC0ientHandler Active");
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
NettyChannel nChannel = attr.get();
if (nChannel == null) {
NettyChannel newNChannel = new NettyChannel("HelloWorld0Client", new Date());
nChannel = attr.setIfAbsent(newNChannel);
} else {
System.out.println("channelRead attributeMap 中是有值的");
System.out.println(nChannel.getName() + "=======" + nChannel.getCreateDate());
}
System.out.println("HelloWorldClientHandler read Message:" + msg);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
handler2:
package com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap;
import static com.lyncc.netty.attributeMap.AttributeMapConstant.NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.Attribute;
import java.util.Date;
public class HelloWorld2ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
NettyChannel nChannel = attr.get();
if (nChannel == null) {
NettyChannel newNChannel = new NettyChannel("HelloWorld2Client", new Date());
nChannel = attr.setIfAbsent(newNChannel);
} else {
System.out.println("channelActive attributeMap 中是有值的");
System.out.println(nChannel.getName() + "=======" + nChannel.getCreateDate());
}
System.out.println("HelloWorldC2ientHandler Active");
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
NettyChannel nChannel = attr.get();
if (nChannel == null) {
NettyChannel newNChannel = new NettyChannel("HelloWorld0Client", new Date());
nChannel = attr.setIfAbsent(newNChannel);
} else {
System.out.println("channelRead attributeMap 中是有值的");
System.out.println(nChannel.getName() + "=======" + nChannel.getCreateDate());
}
System.out.println("HelloWorldClientHandler read Message:" + msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
我们先运行服务器端:

客户端控制台:

这说明每个ChannelHandlerContext上的AttributeMap是相互不影响的
2)测试Channel上的AttributeMap:
我们只需要把2个channel获取Attribute的方法改下就可以了:
Attribute<NettyChannel> attr = ctx.channel().attr(NETTY_CHANNEL_KEY);
两个channel共有四处需要修改,改成获取channel后获取attribute:
再次运行:

好了,首先在ChannelHandler1中赋值了,然后在channelHandlerHandler2中的channelActivew打印了attributeMap中有值了,然后都能够在channelRead中读取到最新值
关于AttributeMap的一些内幕详解,参考一下: